Leaderboard
Popular Content
Showing content with the highest reputation on 13/06/24 in all areas
-
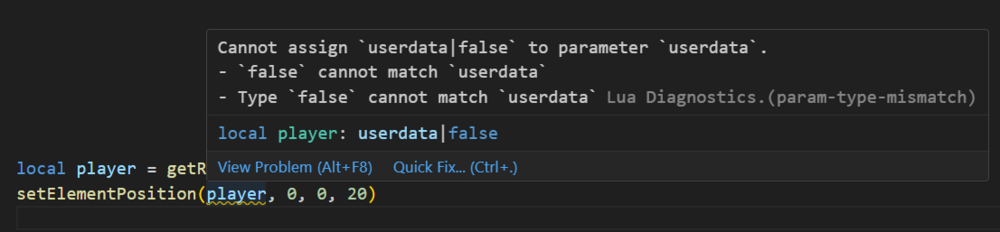
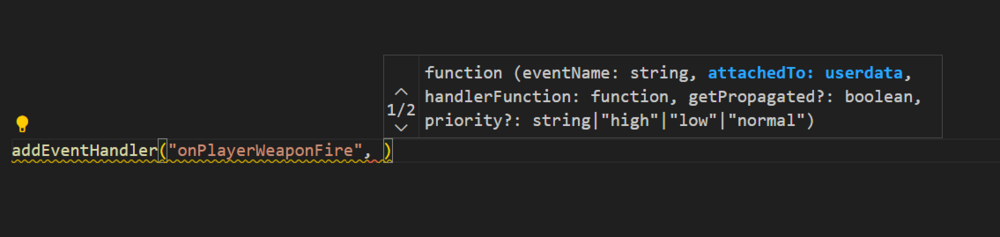
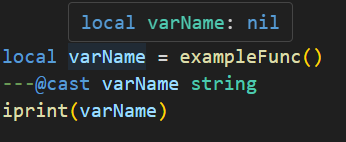
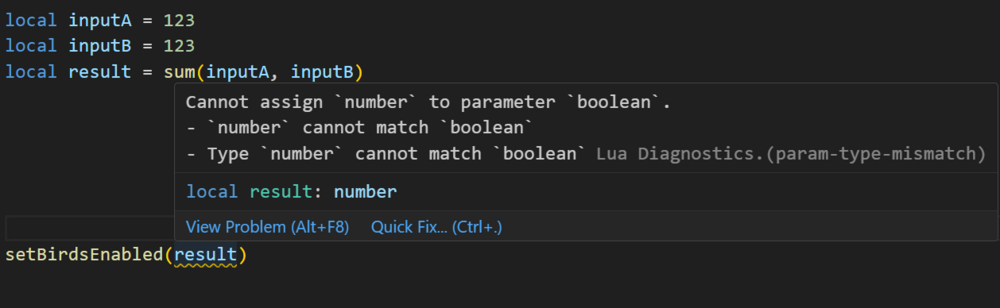
Lua Language Server - Definition files The Lua language server is a powerful tool that enhances the development experience for Lua programming. It provides a comprehensive set of code editing features, including suggestions, auto-completion, and error checking. With the Lua language server, developers can effortlessly navigate through their resource files, access documentation easily, and ensure code correctness by giving warnings. Why should you care? The language server will inform you about all sorts of problems: type mismatches, missing function arguments, missing variables, etc. You have access to a lot of MTA syntax/autocomplete out of the box. The syntax information will remain while writing. You do not have to restart your resource so often in order to validate if everything is working. Type validation Having value type validation in your code editor is one of the main key features of the Lua Language Server. When working with variables, parameters, and arguments in Lua, you are not restricted to specific value types. This flexibility can make mistakes more likely to happen. However, being able to validate those mistakes instantly saves you a lot of time and frustration. Type annotations for your own functions Adding type annotations to your own functions can help improve validation and catch logic mistakes. It is particularly useful when calling functions from different parts of your code, as the annotations provide clarity on the expected input (arguments) and output (return values). Additionally, comments that are placed above or adjacent to a variable or function are visible when hovering over them in another file or line. This can provide helpful information and context when working with the code. How that looks like: How can I quickly add annotations in less than a second? Open the spoiler: AddEventHandler auto-complete Most MTA addEventHandler functions have full eventName autocompletion. And the attached anonymous function is fully autocompleted and typed as well. Navigation features of Lua Language Server It can be time consuming to find out where a (global) function or variable is located. Being able to jump right to it, saves you a lot of time. Other information which you can find in the readme Installation for the Lua Language Server How to use the definition files? Known issues Make sure to always have an empty new line at the end of your files, as recommended in this issue. Currently, the Lua server language definition files do not have a clear separation between serverside functions/events and clientside functions/events. However, it is possible to enforce this separation for specific functions if needed. outputChatBox--[[@as outputChatBox_server]]("Serverside", player) In certain cases, certain functions in the Lua server language definition files may return multiple types, even if you have selected a different syntax. To handle this situation, you can use the `cast` or `as` notation to explicitly specify the desired type or adjust the returned type. See `Casting and as` syntax below. Casting and as In certain situations, you may have a strong understanding of the type(s) that a variable or expression will have. This is where the keywords "cast" and "as" come into play. These keywords enable you to explicitly specify the intended type, ensuring proper type handling. local varName = exampleFunc() ---@cast varName string local varName = exampleFunc() ---@cast varName string | number local varName = exampleFunc() --[[@as string]] local varName = exampleFunc() --[[@as string | number]] Download The definition files can be downloaded here.1 point
-
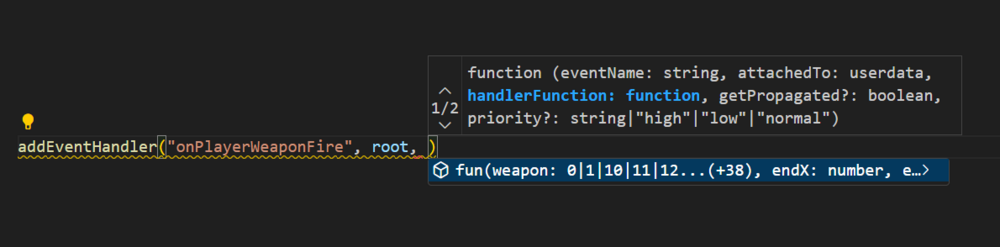
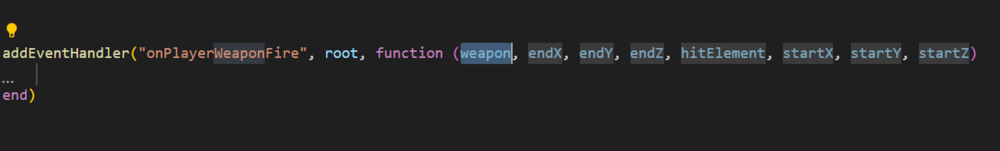
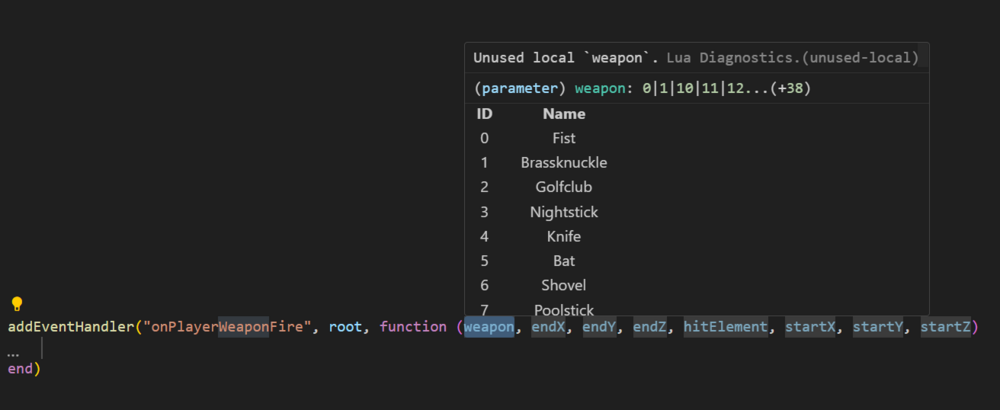
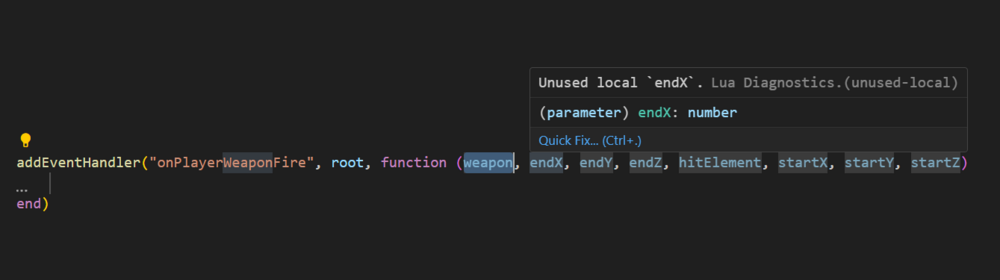
Events tutorial The reason why I created this topic, is that a lot of people are struckeling with them. In this tutorial I will only discus the very basic of them. If you want more, then there is a list of links at the end with more information. If I made any mistakes in the code, please let me know because I am not going to test every part. What are events? (basic description) Events are something custom added by MTA to make it easier to bring scripting(Lua) closer to our game. If we do not have events, then the only thing we can do is give instructions to our game. But our code will never detect changes in our game. The same question again: "So what are the events?" Events are a way to communicate changes in our game to our scripts (or from our scripts). So for example my little ped(cat) gets ran over by a car. Then I really want to know about that, don't I? When an event activates, I describe this as: triggered (from the word trigger) Full wiki information can be found here: Event_system Before we can use events, what do we need to know? There are two things we need to know: The reason why it is triggered. <What happens?/when something happens?> In MTA this is the eventName of the event. (Example: you <ran over> my ped) Who is the one using the event? The event system in MTA is using elements as base (baseElement). This makes it easier to combine the what/when happens? with the one who is related to it. In MTA this is the source of the event. (Example: you ran over my <ped>) Trigger an event A scripting example: (this is not an official event) local ped = createPed( 120, 5540.6654, 1020.55122, 1240.545 ) -- my ped triggerEvent("onPedRanOver", ped) In this example, a custom event gets triggered to tell you that my new created ped has been ranOver. The eventName is "onPedRanOver" and the baseElement is ped. local ped = createPed( 120, 5540.6654, 1020.55122, 1240.545 ) -- my ped local drunkDriver = getRandomPlayer() triggerEvent("onPedRanOver", ped, drunkDriver) In this SERVERSIDE example, I am also adding an extra argument drunkDriver to use the player that ran over the ped. This is not required, but it makes it more complete. See syntax. Syntax bool triggerEvent ( string eventName, element baseElement, [ var argument1, ... ] ) TriggerEvent Receiving triggers Receiving triggers is a bit more complicated, because there are a lot of options for it. You can receive events by listening to them. It is like: You know that something is going to happen but you do not know when. The first step that you have to take is related to this question: "Do I want to receive a custom or not custom event?" Custom events are self created events. They only exist when a scripter makes them. Two lists of NOT CUSTOM EVENTS but default MTA events, serverside and clientside: Server_Scripting_Events Client_Scripting_Events Do I want to receive a CUSTOM event? In case of a custom event, you have to register/enable it first. If you do not enable it and trigger it, you will receive a warning/error about that in your debug console. Syntax bool addEvent ( string eventName [, bool allowRemoteTrigger = false ] ) AddEvent The example below, shows you how to enable a custom event only for trigger events within the same server/client side. addEvent("eventName") -- Is the same as: addEvent("eventName", false) If you put the second argument to false or not fill it in, this means that you can't communicate from the other server/client-side. This option is most likely used for security reasons. Some events shouldn't be able to trigger by the other side For example, worst case scenario: (remote events enabled for a default MTA event) Serverside code: addEvent("onPlayerWasted", true) Clientside code: triggerServerEvent("onPlayerWasted", player, 0, localPlayer, 0, 9, false) OnPlayerWasted If this event is enabled for remote trigger events, then it might be possible to cheating kills/deaths score. Of course, it is not likely that players can run their own clientside code, but it is not impossible in case of not trust able community resources. Enable a custom event for trigger events that crossing sides (From clientside to serverside. From serverside to clientside). addEvent("eventName", true) This event can now be used by remote trigger event functions. See list: Client to server TriggerClientEvent TriggerLatentClientEvent Server to client TriggerServerEvent TriggerLatentServerEvent Enable the event from our previous example: addEvent("onPedRanOver", false) local ped = createPed( 120, 5540.6654, 1020.55122, 1240.545 ) -- my ped local drunkDriver = getRandomPlayer() triggerEvent("onPedRanOver", ped, drunkDriver) If you do not use cross triggering, then I recommend to use the addEvent function in the same resource as where you are going to trigger from. This makes sure that the event is already added and that you will never receive this kind of error/warning "Event isn't added". If you put it in another resource which hasn't started yet, then after triggering you would still receive that error/warning. Start listening The next step is to add the addEventHandler. This function is used to listen to events. When an event is triggered, this handler(addEventHandler) will call the function you have attached to it, in MTA this function is called the handlerFunction. Syntax bool addEventHandler ( string eventName, element attachedTo, function handlerFunction [, bool getPropagated = true, string priority = "normal" ] ) AddEventHandler Resource 1 addEvent("onPedRanOver", false) local ped = createPed( 120, 5540.6654, 1020.55122, 1240.545 ) -- my ped local drunkDriver = getRandomPlayer() triggerEvent("onPedRanOver", ped, drunkDriver) Resource 2 function handlerFunction () end addEventHandler("onPedRanOver", root, handlerFunction) The first 3 arguments, the require ones: eventName attachedTo handlerFunction Making sure that the addEventHandler options are correct set-up. Resource 1 addEvent("onPedRanOver", false) local ped = createPed( 120, 5540.6654, 1020.55122, 1240.545 ) -- my ped local drunkDriver = getRandomPlayer() triggerEvent("onPedRanOver", ped, drunkDriver) Resource 2 function handlerFunction () end addEventHandler("onPedRanOver", root, handlerFunction) There are two conditions for an eventHandler to call the handlerFunction. 1. The event has to be exactly the same. In this case the event "onPedRanOver" is the same in both resources. 2. In both functions, triggerEvent and addEventHandler is an element being used. This element has to be exactly the same. (from where you trigger as well as where you receive) <OR> The triggered element from resource 1, has to be a CHILD of the element in resource 2. The root element is the very top layer of the MTA element structure. It will accept all elements you want to use for your events. See the element tree: If you do not understand the element tree please read this page: Element_tree Source variable The source of an event is the element that triggers the event. This variable isn't passed as an parameter, but it is predefined. This means that it is already created before hand. Some predefined variables do only exist under special conditions. The source variable is one of those, it is a hidden and local variable which is only available when a function is called by an event. List of predefined variables. addEvent("onPedRanOver", false) -- local ped = createPed( 120, 5540.6654, 1020.55122, 1240.545 ) -- my ped local drunkDriver = getRandomPlayer() triggerEvent("onPedRanOver", ped, drunkDriver) function handlerFunction (drunkDriver) iprint(source) -- ped element end addEventHandler("onPedRanOver", resourceRoot, handlerFunction) In this example the ped is the source. See how those two code blocks are connected: addEvent("onPedRanOver", false) -- local ped = createPed( 120, 5540.6654, 1020.55122, 1240.545 ) -- my ped local drunkDriver = getRandomPlayer() triggerEvent("onPedRanOver", ped, drunkDriver) function handlerFunction (drunkDriver) iprint(source) -- ped element end addEventHandler("onPedRanOver", resourceRoot , handlerFunction) resourceRoot In some examples, you see people use the resourceRoot instead of the root element for their addEventHandlers. The resourceRoot is an element created by a resource. This element holds all elements of that resource as (in)direct children. In the example above, the resourceRoot as baseElement will not work, because there are two resources. Each resource has it's own resourceRoot element. The resourceRoot is accessible with the same keyword: resourceRoot, but if you were to inspect the element in multiple resources, then the user data (element identifier) value is not the same. outputChatBox(inspect(resourceRoot)) If we were to put everything in one resource, then it would work: ? addEvent("onPedRanOver", false) -- function handlerFunction () end addEventHandler("onPedRanOver", resourceRoot, handlerFunction) -- local ped = createPed( 120, 5540.6654, 1020.55122, 1240.545 ) -- my ped local drunkDriver = getRandomPlayer() triggerEvent("onPedRanOver", ped, drunkDriver) In case of remote triggering, the resourceRoot in serverside and clientside is considered the same.(As long as they are part of the same resource) Why/when would we use resourceRoot? 1. Limit eventHandlers to the resource elements If you have 1000 markers in your server. One of the resources is for example a trucker mission, where you can get money by hitting markers. The resourceRoot element will make sure that the onMarkerHit event will only trigger for markers created by that resource. addEventHandler("onMarkerHit", resourceRoot, function () -- source element is the marker end) OnMarkerHit 2. Another benefit is that you are able to re-use the same eventNames. Resource 1 addEvent("onPedRanOver", false) function handlerFunction () end addEventHandler("onPedRanOver", resourceRoot, handlerFunction) -- local ped = createPed( 120, 5540.6654, 1020.55122, 1240.545 ) -- my ped local drunkDriver = getRandomPlayer() triggerEvent("onPedRanOver", ped, drunkDriver) Resource 2 addEvent("onPedRanOver", false) function handlerFunction () end addEventHandler("onPedRanOver", resourceRoot, handlerFunction) -- local ped = createPed( 120, 5540.6654, 1020.55122, 1240.545 ) -- my ped local drunkDriver = getRandomPlayer() triggerEvent("onPedRanOver", ped, drunkDriver) These two resources do use the same event, but will not trigger each other their addEventHandlers. Warning: If root was used, then they will!!!! ;@ Lets cross triggering with resourceRoot! Clientside triggerServerEvent("example", resourceRoot) Serverside addEvent("example", true) -- second argument is true! cross triggering enabled! addEventHandler("example", resourceRoot, function () end) getPropagated In this bigger example we will be talking about the option getPropagated. If this option is disabled, it will not detect children any more. Keep reading! After that start code scanning from A, to B and then to C. Syntax addEventHandler bool addEventHandler ( string eventName, element attachedTo, function handlerFunction [, bool getPropagated = true, string priority = "normal" ] ) Example: Clientside -- A triggerServerEvent("onClientPlayerLoaded", resourceRoot) -- trigger an event to serverside --------------------------------------- -- C addEvent("onResponseServer", true) -- first listener addEventHandler("onResponseServer", resourceRoot, function () outputChatBox("getPropagated enabled") end, true) -- getPropagated true by default. -- second listener addEventHandler("onResponseServer", resourceRoot, function () outputChatBox("getPropagated disabled") end, false) -- getPropagated is false. Serverside -- B addEvent("onClientPlayerLoaded", true) -- second argument is true! cross triggering enabled! addEventHandler("onClientPlayerLoaded", resourceRoot, function () --[[ client is a predefined variable, which represents the client/player that communicates with the server More information about predefined variables: https://forum.multitheftauto.com/topic/33407-list-of-predefined-variables/ ]] triggerClientEvent(client, "onResponseServer", resourceRoot) -- first trigger event local element = createElement("randomElement") -- making a randomElement triggerClientEvent(client, "onResponseServer", element) -- second trigger event end) How does this this code works? A. When a client his code has been started, it will execute a triggerServerEvent. (It doesn't wait for any other clientside files to be loaded) B. The server receives the event. And sends two triggerClientEvents back: The first one is using the resourceRoot as baseElement. The second one is using a randomElement as baseElement. Both are using the event "onResponseServer" C. There are two addEventHandlers listening to the event: "onResponseServer" The first one is using getPropagated and the second one is not using getPropagated. The randomElement that is created, is by default an indirect child of the resourceRoot of the same resource. What will happen? When firing the first trigger event, both listeners will call their handlerFunction. But when firing the second trigger event, only the first listener will call it's handlerFunction. The randomElement is an indirect child of resourceRoot, but because getPropagated is disabled it will not call it's handlerFunction. Other tutorials related to this one: See also this tutorial about deeper limiting event ranges within your resource and reducing addEventHandlers https://forum.multitheftauto.com/topic/100069-tut-addeventhandler-on-a-group-of-elements-small-tutorial/ More information Full wiki information: Event_system A list of more information about triggering events: (Client to client / server to server) TriggerEvent Client to server TriggerClientEvent TriggerLatentClientEvent Server to client TriggerServerEvent TriggerLatentServerEvent A list of more information about receiving events: AddEvent AddEventHandler RemoveEventHandler Two lists of MTA events, serverside and clientside: (warning: not custom events) Server_Scripting_Events Client_Scripting_Events Cancel events CancelEvent WasEventCancelled (warning: custom events ONLY) GetCancelReason (Server only) Cancel latent events and their status GetLatentEventHandles CancelLatentEvent GetLatentEventStatus1 point
-
1 point